How to select and size an vibration motor?
Rotary vibrators or linear force vibration motor are widely used to initiate or restore the flow of stored bulk materials, and have proven to be effective in most situations. Industrial vibrators are available in many types and sizes. The key factors in using them effectively are to select the proper type and size of vibrator for your specific application, and to ensure that the vibrator is properly mounted.
Selecting an industrial vibration motor for your application
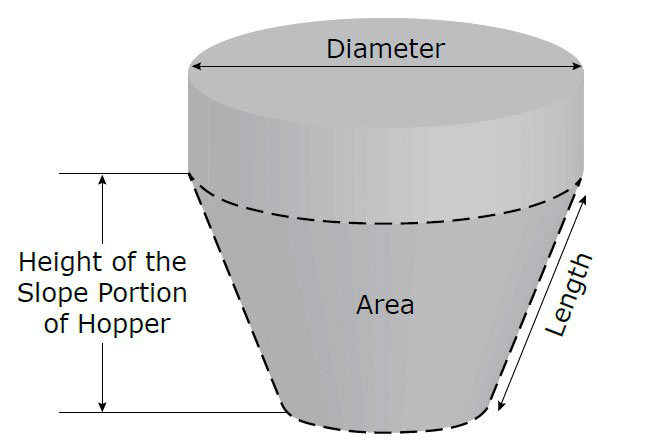
The first consideration in selecting an industrial vibration motor is to determine the mass of the bulk material that must be vibrated. To do this, first determine the volume and weight of the material in the sloped portion of the hopper (Note: If optimum flow is achieved with the material in the sloped portion of a properly designed hopper, the remaining materials will flow properly.)
A five step approach to selecting an industrial vibrator
1. Using the “Global Calculators” select the style of the hopper and enter the dimensions of the sloped portion of the hopper as indicated.
2. Enter the density of the bulk solid stored in the hopper.
3. Select the appropriate weight to force ratio.
a. If the bulk material is less than 90 lb/ft3 or flows freely in normal conditions, select a ratio of 1lb force/10 lb material.
b. If the bulk material is greater than90 lb/ft3or is sticky, has high moisture content, or bridges easily, select a ratio of 1 lb force/5 lb material.
c. If the bulk material has characteristics of both a and b, e.g., bulk material that is heavier than 90 lb/ft3, but tends to flow easily, or materials that are lighter and often bridge or cling in normal conditions, use a ratio of 1 lb force/8 lb material. Note: These ratios are approximations based on field experience. While not an absolute rule, they have been proven effective in properly selecting the vibrator size.
4. To select the most effective vibration motor, you should match the characteristics of the stored materials with the appropriate style vibrators. Bulk materials respond to the energy produced by Industrial Vibrators. This energy is comprised of Frequency (how rapidly the waves of energy cycle)and Amplitude (the height of the waves). The combination of these factors is calculated as force and typically expressed (in the USA) in pounds (or force-pound or pound-force). Generally speaking, finer materials respond more favorably to higher frequency vibration, while higher force is more effective on coarser materials.
5. Select your preferred Power Source (pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric) and refer to the product performance data to select one or more well-matched vibrators with a force output equal to or slightly greater than the force as determined using the appropriate weight-to-force ratio., based on 10: 1 weight-to-force ratio, to choose a vibrator as indicated in the guide. Other important factors to consider when selecting vibration motor.
If your stored material is best categorized as coarse, you may achieve the best results using a Linear Vibrator (pneumatic piston) or a higher force Rotary Vibrator (motor-driven hydraulic, pneumatic or electric).
Finer materials are more likely to respond to higher frequency Rotary Vibrators (pneumatic turbines or ball vibrators).
Follow all recommended mounting instructions. A properly-mounted vibrator will effectively transfer the energy to the bulk material and will provide better performance, longer vibrator service life and minimize stress on the hopper. The calculated vibrator force does not need to exactly match the output of the selected vibrator. For example, if the calculated force requirement is 1,000 force-pounds (4.45 kN), you can use a vibrator with1, 200 force-pounds (5.34 kN) rating. In addition, the speed of hydraulic and pneumatic vibrators can be adjusted by reducing the flow of hydraulic fluid or compressed air. This reduction of speed will reduce the force the vibrator produces, allowing for additional “fine-tuning” of the vibrator’s frequency and force.
If a Linear Vibrator (piston) is selected, additional important considerations are bin wall thickness and bin capacity. Piston Vibrators restore material flow by producing a linear shock wave that reduces friction and forces the bulk material away from the hopper wall. To avoid damage to the hopper, do not use a larger piston vibrator than the bin wall thickness recommendations.
